React state management continues to evolve, presenting both new challenges and opportunities for developers in 2026. Managing state efficiently has always been one of the biggest hurdles with the React framework.
And it isn’t just the users who are affected by it. React developers need a modern, scalable, and maintainable state management process for designing efficient and complex user experiences.
Developers use React hooks to access and share component states across different components. However, when dealing with a large number of components, the complexity becomes too much for React hooks to handle.
As React applications grow in scale and complexity, choosing the right state management tool becomes critical for performance, maintainability, and long-term success.
Developers need to leverage React state management libraries in such cases.
But how do you choose the state management library that’s best for you? It depends. You need to consider factors like scalability, performance, and ecosystem support. Let’s learn more about the most important libraries available and how you should approach your decision.
7 Top React State Management Libraries
There are more than 90 React state management libraries on GitHub. However, based on a number of key characteristics, some stand out amongst the rest.
The following factors should go into your decision when choosing the right state management library for your next React app:
- Usability
- Performance
- Scalability
- Modifiability
- Maintainability
- Reusability
- Testability
- Ecosystem
- Community
We’ve researched almost all the available React state management libraries, so you don’t need to, and narrowed it down to just seven for 2026.

1. Redux
Redux has been around since 2015, but it is definitely still relevant in 2026. The very first React state management library, React, was created to simplify state management by centralizing the state repository. It does this by using a ‘Store’ to hold all the states of your application.
Over the years, Redux has evolved significantly, with the introduction of Redux Toolkit providing a streamlined approach to state management.
Redux Toolkit reduces boilerplate, simplifies reducers, and improves the overall developer experience. However, even with these enhancements, Redux can still feel cumbersome due to the need for multiple actions, reducers, and providers.
Redux still maintains a comfortable lead over all other state management libraries, according to the results of the Jan 2025 npm trends. Redux works using actions and reducers. Actions are objects instructing the store on what events should take place. And reducers are functions that are executed based on the action’s input and an object’s initial state.
Whenever you need to modify the state of a component based on user behavior, you can dispatch an action to the reducer, which changes the state and saves it in the store.
Cons of Redux
Though Redux is widely popular, developers aren’t too keen on the related boilerplate they need to work with.
One of our developers here at Trio has even commented that the amount of boilerplate required to get something working with Redux feels like serious over-engineering. However, this same developer also notes that there are tools like ‘createSlice’ from Redux Toolkit that help minimize this.
Here’s what some code from a simple counter app might look like. Take note of all the boilerplate code required:
// store.js
import { configureStore, createSlice } from ‘@reduxjs/toolkit’;
const counterSlice = createSlice({
name: ‘counter’,
initialState: { count: 0 },
reducers: {
increment: (state) => { state.count += 1; },
decrement: (state) => { state.count -= 1; },
reset: (state) => { state.count = 0; },
},
});
export const { increment, decrement, reset } = counterSlice.actions;
export const store = configureStore({ reducer: counterSlice.reducer });
As you can see, multiple actions and reducers lead to a lot of code that gets hard to maintain when apps become complex. However, the Redux Toolkit can be used to reduce the boilerplate and simplify the overall issue.
This also makes the library very difficult and time-consuming to learn.
Pros of Redux
With the Redux Toolkit taking care of the usability of Redux, its simple logic and pure functions make it quite maintainable, performant, and testable. You can also modify and reuse Redux code as it is framework-agnostic and supports middleware. This means that you can use its logic outside of React.
Due to its maturity, it enjoys a large community of developer support and a rich ecosystem of add-ons and tools, including some incredibly powerful debugging tools.
Overall, it’s a great option if you are working with large-scale applications with complex state logic.
2. Recoil
Recoil, released in early 2020, is relatively new compared to some other options out there. Recoil is known for being developed by Facebook and its React-like approach to state management.
The biggest difference between Recoil and Redux is that, while Redux uses centralized state management, Recoil lets individual components subscribe to small, independent pieces of state. This can make it quite efficient.
The main concepts used in Recoil are atoms and selectors. An atom is a shared-state unit that represents a single-state property. A component can subscribe to an atom to get its value. Atoms are similar to React’s local state, but with the added benefit of being shared among different components.
Selectors are pure functions that get their value from atoms or other selectors. Their value is recomputed whenever the atoms or selectors they’re subscribed to change their own values.
This way, Recoil tracks which components use which atoms/selectors, so it can re-render a component only if its connected atom/selector changes its value. This technique makes Recoil incredibly performant and scalable.
Pros of Recoil
There are many reasons why Recoil is second on our list, the foremost of which is the fact that it is very lightweight and performant, with minimal re-renders required. This allows you to improve app performance.
You can also integrate it with React Suspense, which allows you to optimize for concurrent rendering. This means it scores exceptionally well on modifiability and maintainability.
Since there is a lot less boilerplate code than something like Redux, partly thanks to its more intuitive API, Recoil is easier for developers to work with and also a lot easier for developers new to React state management to learn.
Cons of Recoil
With all its benefits, Recoil is relatively new and doesn’t have a sizeable community and ecosystem. When we consulted our developers, we realized this isn’t going to change any time soon. You might even struggle to find developers who have had experience in Recoil, as they are few and far between.
It’s also React-dependent and can’t be reused elsewhere.
However, because it isn’t so popular – even several years after its release – and its long-term stability is still unclear, we would really recommend that you think twice before adopting it.
Overall, our developers would recommend the use of Recoil in applications that require a shared state with fine-grained state management and minimal performance overhead.
3. Zustand
Built by the people behind Jotai and weighing in at under 1KB, Zustand might be the smallest library on this list. It is a very lightweight and minimalistic alternative to something like Redux. But it’s certainly nothing to be scoffed at. Zustand brings a simple and minimalistic API that makes it fast and scalable.
Zustand’s API is based on hooks, and React components can then be used to retrieve and share state. This allows developers to manage state with less code while maintaining a scalable and performant architecture.
Pros of Zustand
Zustand easily overcomes common issues in React, such as the ‘zombie child problem,’ React concurrency, and context loss between mixed renderers. It claims to be the only state manager that has managed to do so.
It renders components only if their state changes and provides clean and easily maintainable code that’s much shorter and more readable than many other libraries on this list. It natively supports asynchronous functions, making it easier to manage the async state than vanilla Redux.
Zustand can also manage transient state updates without re-rendering the components.
Our developers have commented that Zustand couldn’t be simpler. It follows a composition approach that is already familiar to every React developer and doesn’t require the extra effort of something like Redux.
It seems this sentiment is shared by many, as Zustand has managed to gain more than 50.2k stars on GitHub, which is more than Rematch, Jotai, and MobX.
Take the simple counter application from above again. This is what it would look like in Zustand. Notice how much less boilerplate code is required:
// store.js
import { create } from ‘zustand’;
export const useCounterStore = create((set) => ({
count: 0,
increment: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count + 1 })),
decrement: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count – 1 })),
reset: () => set({ count: 0 }),
}));
Cons of Zustand
One limitation that we have noticed is that Zustand has very little middleware support. This might make it less suitable for applications that require more advanced state management capabilities, such as undo/redo functionality or structured event handling.
Overall, it is still a great choice for small to medium-sized companies that need something simple and effective for state management.
4. Jotai
Jotai was announced in 2021 and is another library that implements atomic state management and has a very simple and intuitive API.
Each atom – or unit of state – can be read and updated separately, so you only re-render components when their specific atom changes.
Pros of Jotai
It has many of the benefits of other similar libraries, like performance and simplicity, as well as integration with React Suspense and other libraries on this list.
However, its standout features include its smaller size, cleaner API, greater TypeScript support, and deeper maturity.
Thanks to its garbage collection, Jotai is extremely performant. It doesn’t require keys and depends on JavaScript to track its atoms. This leads to automatic garbage collection and optimized memory usage.
Jotai goes one step further in atomic state management by handling pretty much everything like an atom. Developers can also compose atoms together to create reactive state dependencies without needing to use excessive boilerplate.
Cons of Jotai
Jotai may require additional setup for more complex scenarios. This can include situations like global state synchronization across deeply nested components.
Its decentralized nature can make state logic scattered and difficult to manage as an application scales. Similarly, if your developers are not mindful of how their atoms are structured, excessive dependencies could end up making debugging more difficult and time-consuming.
As Jotai isn’t as popular as some other libraries, you may also run into issues with long-term adoption and finding developers who can provide long-term support.
Overall, it’s a strong contender if you have a smaller project that needs flexible, reactive, and modular state management.
5. MobX
Outside Redux and React’s built-in Context API, MobX is probably the most popular state manager out there. MobX takes a markedly different approach to state management than Redux.
Instead of relying on actions and reducers, it follows the OOP paradigm (or observer-observable paradigm) and uses the observer/observables pattern to manage the state.
MobX creates an observable data model that your observers or components can refer to. It then tracks the data accessed by each component and renders it whenever the data changes.
Another feature of MobX is immutability. The strict mode options MobX provides allow you to update the state silently to avoid side effects.
Pros of MobX
MobX is exceptionally easy to work with in terms of developer experience. This makes it a great option if your focus is on long-term job satisfaction and performance.
Usability, performance, and scalability are no problems for MobX. But it also excels in modifiability and reusability. And being a mature library (27.7k stars on GitHub), MobX has no lack of community support or a fledgling ecosystem.
There are many reasons for this, but one of the biggest advantages of MobX is the automatic state tracking. Instead of having to manually dispatch actions and update reducers, like you would have to in Redux, this is automated in MobX.
The library is also framework-agnostic and can be used outside of React.
Cons of MobX
As it doesn’t require actions or reducers, any modifications in the state are instantly reflected in components. This makes MobX truly reactive. But this also means shorter and less explicit code. This might be a con for some developers as it takes away some visibility and control from them.
Reactivity issues are also fairly common if your developers are not very familiar with MobX. Similarly, MobX’s more dynamic approach can make it harder to maintain large-scale applications if state dependencies are not well-structured.
Overall, MobX is a good option if you are working on applications that need highly dynamic user interfaces and if your developers prefer less boilerplate code.
6. XState
XState takes a completely different approach to state management from all the other libraries on this list by using state machines and statecharts. In doing this, XState enforces explicit state transitions, making it highly structured and predictable.
Since all state transitions are explicitly defined, it becomes much easier to manage complex workflows and ensure that the application behaves as expected. This makes XState particularly useful for state-driven applications, such as multi-step forms, wizards, and animations.
Pros of XState
XState’s biggest advantage is that it provides a clear visualization of state transitions. For the layman, this means you can easily track and debug the state. It also allows for finite state management, so each state is well-defined, making it easier to manage.
XState also supports hierarchical state machines, meaning developers can nest state logic within different components. The organization that this lets developers use makes it an excellent tool for structuring large applications with intricate logic.
Another advantage is that XState works well with any frontend framework, not just React. Like with many other options, this is important to consider as it gives you options later.
Cons of XState
The biggest downside to XState is its steep learning curve. Since XState has a unique way of functioning, with finite state machines and transitions, developers may struggle.
Additionally, while XState excels at managing complex state logic, it can be overkill for simpler applications, where it will overcomplicate things unnecessarily.
Overall, XState is an excellent choice for applications with intricate workflows, such as multi-step processes, form validation, and complex UI interactions.
7. Valtio
Valtio is a proxy-based state management library. It lets developers work with mutable state while still benefiting from React’s reactivity. This makes it a lightweight and easy-to-use alternative for developers who prefer direct state manipulation without needing to define actions or reducers.
Like some of the other options that we have already discussed, Valtio automatically tracks changes to the state and updates only the necessary components, which can be very efficient.
Pros of Valtio
Valtio has a very minimalistic API. Developers don’t need to worry about defining complex state logic. This promotes fast development cycles.
Since Valtio is proxy-based, there are no boilerplate-heavy state updates. This makes it more intuitive.
Additionally, Valtio supports automatic reactivity, ensuring that components are only re-rendered when necessary.
The derived state and snapshot features allow developers to efficiently compute and store the state when needed. This makes it particularly useful for applications that track and manipulate transient state data.
Cons of Valtio
One of the biggest challenges with Valtio is its smaller community and ecosystem. It does not have many third-party tools, integrations, or widespread adoption. This means that, even if you are able to find developers, they may struggle to find extensive documentation or community support when working with the library.
It’s also not the best choice for applications that require strict state predictability or structured event handling. Valtio’s flexibility can lead to unexpected behavior if the state is not managed carefully.
Another potential downside is that Valtio is less suitable for large-scale applications where strict state organization and lots of middleware are required.
Overall, Valtio is best suited for small to medium-sized projects where simplicity, flexibility, and direct state manipulation are important.
Comparison Table of State Management Libraries
| Libraries | Performance | Scalability | Ease of Integration | Community Support |
| Redux | High and predictable. | Large-scale application suitability. | Moderate. | Most extensive. |
| MobX | High | Fine-grained state only. | Easy. | Large and active. |
| Zustant | Very high | Small to medium application suitability. | Very easy. | Growing and already reasonable. |
| Jotai | High | Good scalability. | Easy. | Growing but still minimal. |
| Recoil | Good for concurrent rendering | Medium to large application suitability. | Moderate. | Growing but still minimal. |
| XState | High | Excellent scalability. | Steep learning curve. | Stable. |
| Valtio | Very high | Small to medium application suitability. | Very easy. | Minimal. |
Understanding React State Management
What Is React State Management?
State represents the part of a component that is variable depending on the user’s action. It’s a JavaScript object that acts as the memory of the component, storing many of its properties. React state management, therefore, is the process of sharing data across different components.
When a user interacts with your React app, changes can occur in the state of one or more components. These changes can affect the user interface (UI) presented to the user, and hence, you need to manage them effectively.
Why Is React State Management Important?
State management in React is extremely important to preserve the integrity of a React app by ensuring ease of user experience.
When users are interacting with your React application, their every action can change the state of multiple components on the app. Take, for instance, an e-commerce application where purchasing a product can affect multiple components via the following:
- Adding products to the cart
- Adding products to the customer’s cart history
- Modifying the count of purchased products
In such a scenario, with complex elements interacting with each other and requiring the sharing of states among them, scalability is easily affected. If robust state management libraries aren’t implemented, the task of frequently debugging and fixing the app can quickly become unsustainable.
In small applications, this state management is straightforward, but as applications scale, it can become more complex.
React state management is crucial to help communicate states between multiple components in a way that’s easy, coherent, and scalable.
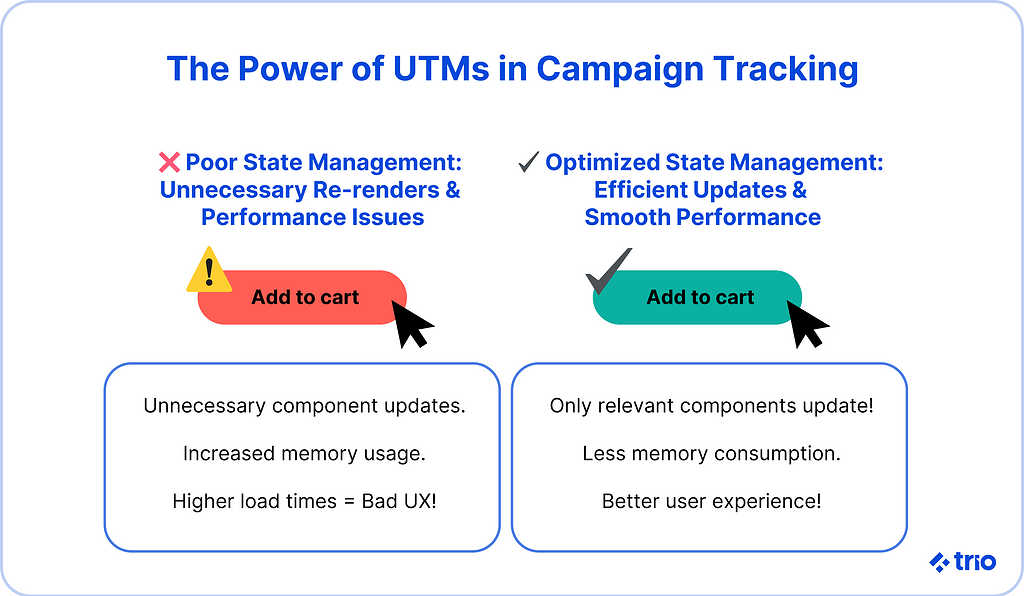
One of the biggest challenges in state management is avoiding unnecessary re-renders, which can negatively impact performance. Without an optimized approach, state changes in one component could trigger updates in unrelated components, leading to laggy interfaces and high memory consumption.
Evaluating React State Management Libraries.
React state management libraries offer novel approaches to tackle state management effectively, helping developers build scalable and highly interactive React applications.
These libraries are modular pieces of code that take care of a lot of the state management best practices for developers. Picking up and perfecting these libraries is fast and easy. Developers have a wide variety of seasoned and new libraries to choose from.
Different state management libraries in React use different approaches to achieve the same solution. They also differ from each other in terms of library size, support for languages, ease of debugging, documentation, API support, and availability of built-in features, like async handling, middleware, caching, and more.
The most common approaches include centralized state management, atomic state management, proxy-based state management, state machines, and state charts.
The library choice will also depend on your specific needs, the size of your development project, and the expertise of your developer team.
How To Choose the Right React State Management Tool
We recommend that you consider several factors to choose the right React state management tool:
- Performance: Assess efficiency and impact on application speed.
- Scalability: Determine suitability for large-scale applications.
- Ease of Integration: Evaluate the learning curve and integration process.
- Community Support: Consider the availability of resources and community engagement.
Every project is different and has its own unique dependencies and business use cases, and fits with one solution over the other. All the alternatives discussed above attempt to solve the same problem with different approaches.
Redux and MobX are old favorites in the community and are natural choices for the majority of projects. Knowing Redux, in general, gives you added benefits during state management in your projects.
But in some cases, other options might be better suited. For instance, Jotai offers an innovative approach to state management and has managed to capture the attention of the community in a short amount of time.
Irrespective of the state management library you choose, you’ll also need to assess the expertise of your development team and their comfort with React in general. And if you’re in the market for React developers, Trio can help you connect with world-class talent in a seamless and highly economical process.
Trio ditches conventional and bloated hiring models and distills the process into a clean and efficient one, taking all the hassle away from you.
Emerging Trends in React Management Libraries
After many years in the industry, we have been able to watch trends rise and fall. At the moment, there are a few that you should be concerned with.
It seems that Atomic state management solutions are becoming more popular. In fact, Zustand and Jotai are some of the best React state management libraries in 2026, thanks to their lightweight nature and their minimalistic APIs.
We’ve also noticed that the integration of state management with React Server Components is becoming more important with the introduction of RCSs. This allows for server-side rendering, which means you can stream components to the client side efficiently, provided that it is done correctly.
Most trends will be focused on performance optimization and sustainable software development. If you continue to focus on those, you will stay at the forefront of innovation. Our developers can help you do just that.
Conclusions
React state management is an ongoing challenge for any React project. Tackling it depends not only on choosing the right state management tool but also on having the right people on your team.
There are many options out there in 2026, but it is important that you assess your project requirements before starting, as not every option is right for each situation. Staying up to date on the latest developments in the React ecosystem will also help you make a decision that works for you now and into the future.
If you want to learn more about hiring senior React developers, contact Trio today and get more done with the best-in-class talent.
